The protein blotting workflow involves selection of the appropriate gel, method, apparatus, membrane, buffer and transfer conditions. Once proteins are immobilised on a membrane, they are available for visualisation, detection and analysis.
There are two main types of electrophoretic blotting apparatus and transfer procedures:
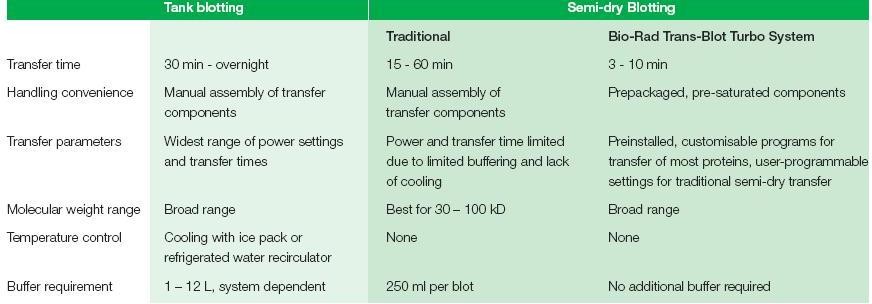
- Tank transfer systems - gels and membranes are submerged under transfer buffer in tanks; these systems are useful for most routine protein work, for efficient and quantitative protein transfers, and for transfers of proteins of all sizes. Tank transfer systems offer the most flexibility in choosing voltage settings, blotting times and cooling options.
- Semi-dry systems - gels and membranes are sandwiched between buffer-wetted filter papers that are in direct contact with flat-plate electrodes; these systems are typically easier to set up than tank systems and are useful when high-throughput is necessary and extended transfer times are not required or when discontinuous buffer systems are used. Active cooling options are limited with semidry blotting.
To learn more, visit www.miniprotean.com
Tags: 2D Gel Electrophoresis, Bio-Rad Laboratories, protein electrophoresis, western blotting